Details of the new ZipperDB
ZipperDB now operates as a fully connected neural network that generates scores for individual hexapeptide sequences. It describes the propensity for that segment to form a type 1 steric zipper. The network was trained on 3.8 million unique hexapeptide sequence and score combinations. For 99% of segments it yields scores that are within 1REU (Rosetta Energy Units) of those anticipated using the original ZipperDB protocol.
We stress that the newly generated scores are not exact replicas of those originally generated by ZipperDB. Nonetheless, the scores generated by the new ZipperDB are highly consistent with those of the original. Most of the scores fall in the error range between ±0.5 Rosetta Energy Units (REU) away from the original scores in the database. The difference between a prediction from the neural network and the original ZipperDB score may be caused by residual errors in the network of the inherent stochasticity of the Rosetta protocol.
Comparative Example
Protein Sequence (42 residues)
Fibrillation Propensity Profile
Original 3D method
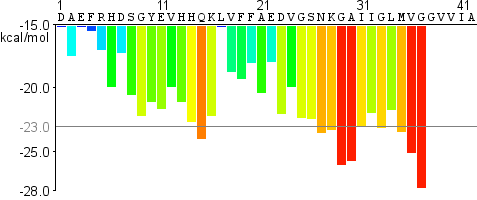
New structure-informed machine learning method
Figure 1 : Comparative example of ZipperDB performance for amyloid-beta. Top plot shows zipper profile using the
original 3D profile method. Bottom plot shows zipper profile using the new, structure-informed machine learning
method.
If you find this database useful, please cite:
Originally: Goldschmidt L, Teng PK, Riek R, Eisenberg D (2010). The amylome, all proteins capable of forming amyloid-like fibrils.
PNAS, 107(8): 3487-3492.
Figure 1 : Comparative example of ZipperDB performance for amyloid-beta. Top plot shows zipper profile using the original 3D profile method. Bottom plot shows zipper profile using the new, structure-informed machine learning method.
Originally: Goldschmidt L, Teng PK, Riek R, Eisenberg D (2010). The amylome, all proteins capable of forming amyloid-like fibrils. PNAS, 107(8): 3487-3492.